Kia Sportage: Components and Components Location | Description and Operation
Components
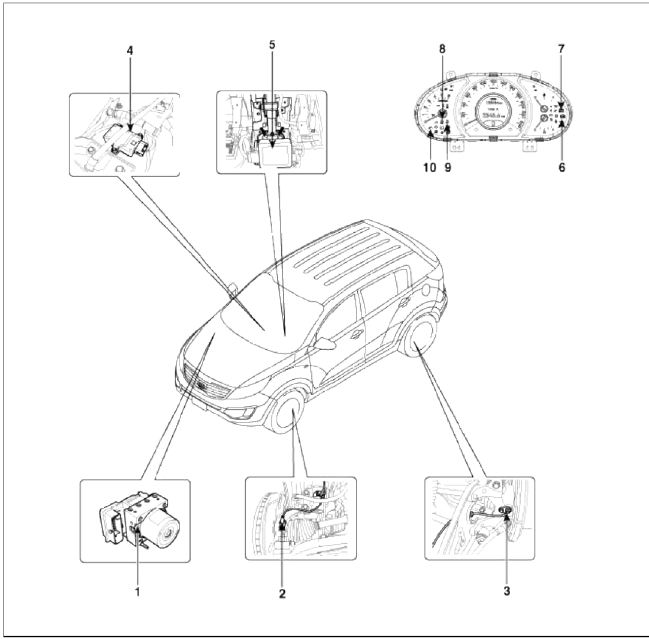
- HECU module
- Front wheel speed sensor
- Rear wheel speed sensor
- Yaw rate & Lateral & Longitudinal G sensor
- Steering angle sensor
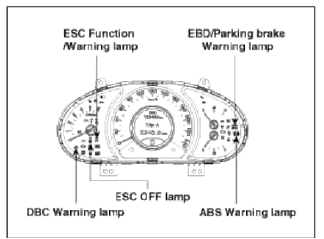
- ABS Warning lamp
- Parking brake EBD warning lamp
- ESC OFF lamp
- ESC Function/Warning lamp
- DBC warning lamp
Description and Operation
Description of ESC
Optimum driving safety now has a name : ESC, the Electronic Stability Control.
ESC recognizes critical driving conditions, such as panic reactions in dangerous situations, and stabilizes the vehicle by wheel-individual braking and engine control intervention.
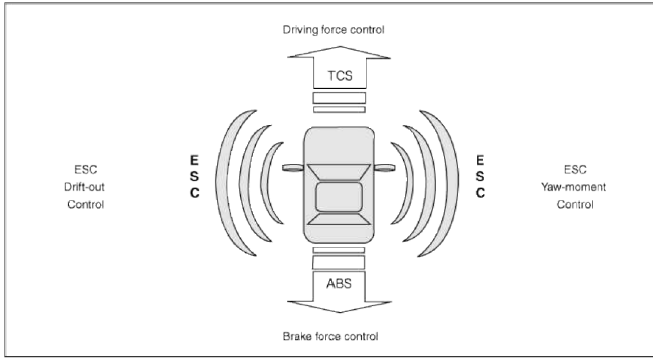
ESC adds a further function known as Active Yaw Control (AYC) to the ABS, TCS, EBD and ESC functions.
Whereas the ABS/TCS function controls wheel slip during braking and acceleration and, thus, mainly intervenes in the longitudinal dynamics of the vehicle, active yaw control stabilizes the vehicle about its vertical axis.
This is achieved by wheel individual brake intervention and adaptation of the momentary engine torque with no need for any action to be taken by the driver.
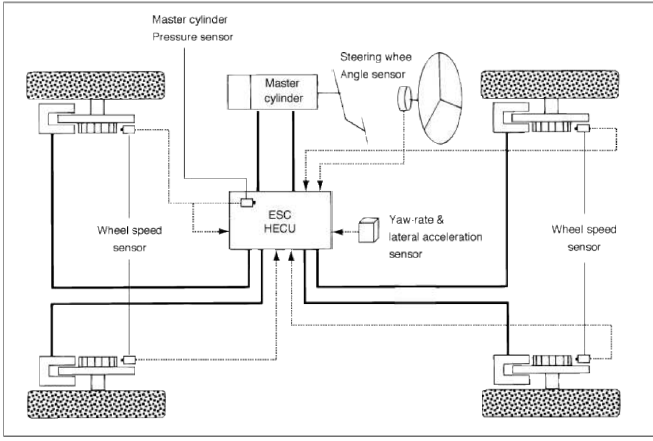
ESC essentially consists of thee assemblies: the sensors, the electronic control unit and the actuators.
The stability control feature works under all driving and operating conditions. Under certain driving conditions, the ABS/TCS function can be activated simultaneously with the ESC function in response to a command by the driver.
In the event of a failure of the stability control function, the basic safety function, ABS, is still maintained.
Description of ESC Control
ESC system includes ABS/EBD, TCS and AYC function.
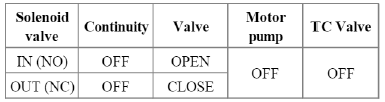
ABS/EBD function: The ECU changes the active sensor signal (current shift) coming from the four wheel sensors to the square wave. By using the input of above signals, the ECU calculates the vehicle speed and the acceleration & deceleration of the four wheels. And, the ECU judges whether the ABS/EBD should be actuated or not.
TCS function prevents the wheel slip of drive direction by adding the brake pressure and engine torque reduction via CAN communication. TCS function uses the wheel speed sensor signal to determine the wheel slip as far as ABS function.
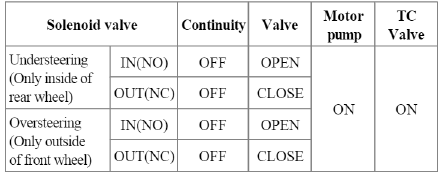
AYC function prevents unstable maneuver of the vehicle. To determine the vehicle maneuver. AYC function uses the maneuver sensor signals (Yaw Rate Sensor, Lateral Acceleration Sensor, Steering Wheel Angle Sensor).
If vehicle maneuver is unstable (Over Steer or Under Steer), AYC function applies the brake pressure on certain wheel, and send engine torque reduction signal by CAN.
After the key-on, the ECU continually diagnoses the system failure. (self-diagnosis) If the system failure is detected, the ECU informs driver of the system failure through the BRAKE ABS/ESC warning lamp, (fail-safe warning)
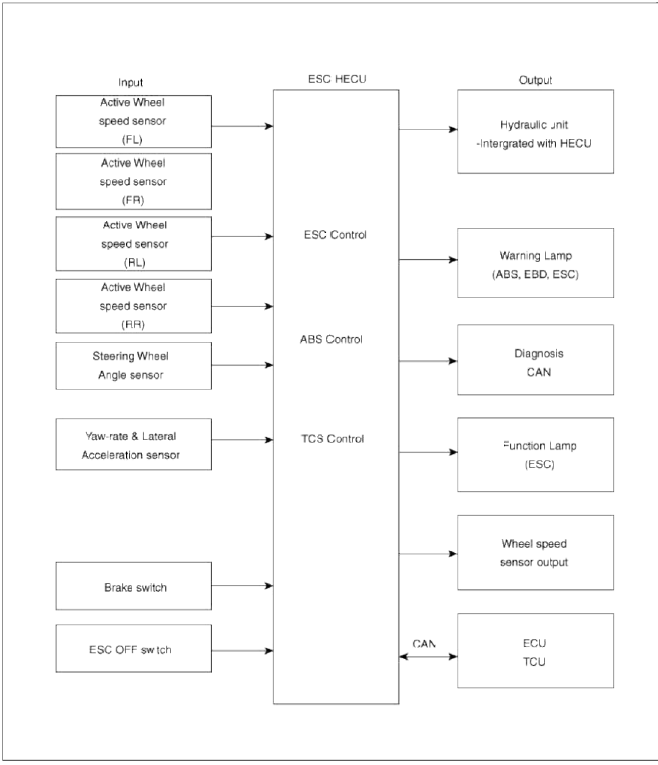
Input and Output Diagram
ESC Operation Mode
ESC Hydraulic System Diagram
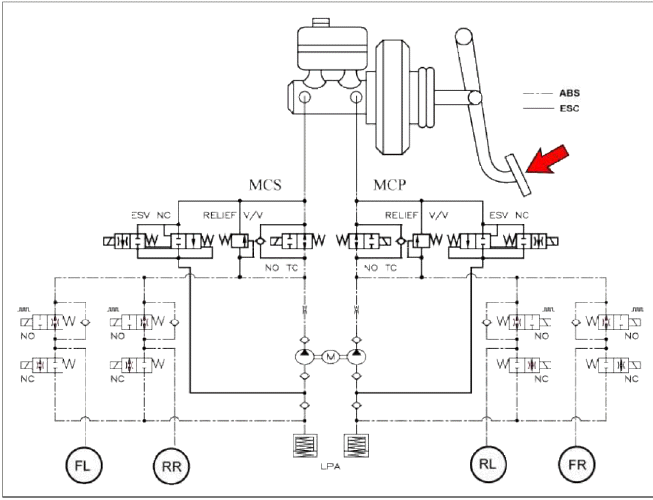
1. ESC Non-operation: Normal braking.
2. ESC operation
ABS Warning Lamp module
The active ABS warning lamp module indicates the self-test and failure status of the ABS. The ABS warning lamp shall be on:
- During the initialization phase after IGN ON. (continuously 3 seconds).
- In the event of inhibition of ABS functions by failure.
- During diagnostic mode.
- When the ECU Connector is separated from ECU.
- Cluster lamp is ON when communication is impossible with CAN module.
EBD Parking Brake Warning Lamp Module
The active EBD warning lamp module indicates the self-test and failure status of the EBD. However, in case the Parking Brake Switch is turned on, the EBD warning lamp is always turned on regardless of EBD functions. The EBD warning lamp shall be on:
- During the initialization phase after IGN ON. (continuously 3 seconds).
- When the Parking Brake Switch is ON or brake fluid level is low.
- When the EBD function is out of order.
- During diagnostic mode.
- When the ECU Connector is separated from ECU.
- Cluster lamp is ON when communication is impossible with CAN module.
ESC function warming lamp (ESC system)
The ESC function warming lamp indicates the self-test and failure status of the ESC.
The ESC function warming lamp is turned on wider the following conditions:
- During the initialization phase after IGN ON. (continuously 3 seconds).
- When the ESC function is inhibited by system failure.
- When the ESC control is operating. (Blinking - 2Hz)
- During diagnostic mode. (Except standard mode)
- Cluster lamp is ON when communication is impossible with CAN module.
ESC Off Lamp (ESC system)
The ESC Off lamp indicates the self-test and operating status of the ESC.
The ESC Off lamp operates under the following conditions:
- During the initialization mode after IGN ON. (continuously 3 seconds).
- ESC Off lamp is On when driver input the ESC Off switch.
ESC On Off Switch (ESC system)
The ESC On/Off Switch shall be used to toggle the ESC function between On/Off states based upon driver input.
The On/Off switch shall be a normally open, momentary contact switch. Closed contacts switch the circuit to ignition.
Initial status of the ESC function is on and switch toggle the state.
DBC Warning Lamp (DBC only)
The DBC warning lamp indicates the self-test, failure and operating status of the DBC function.
The DBC lamp operates wider the following conditions:
- During the initialization phase after IGN1 ON.
- When driver turn on the DBC function by on/off switch.
- hi the event of inhibition of DBC function by failure.
- When the DBC control is operating. (Blinking-2Hz)
- During diagnostic mode. (Except standard mode)
- Cluster lamp is ON when communication is impossible with CAN module.
Schematic Diagrams
Circuit Diagram - ESC (l)
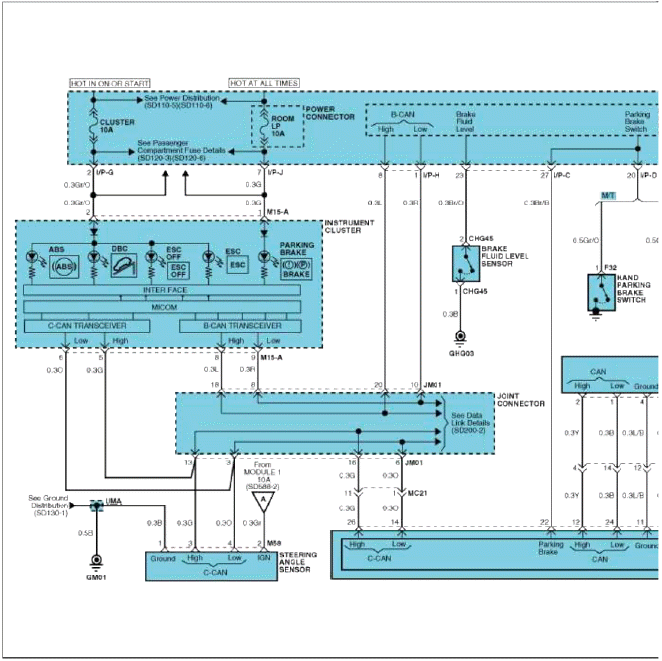
Circuit Diagram - ESC (2)
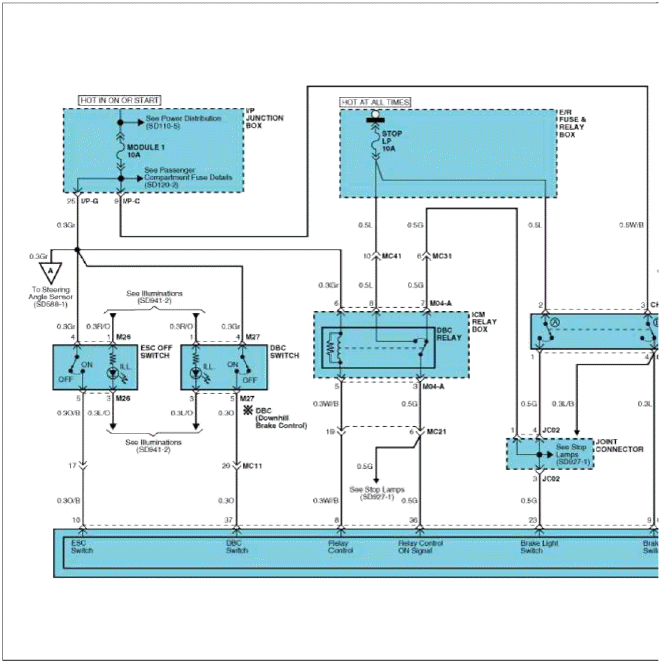
Circuit Diagram - ESC (3)
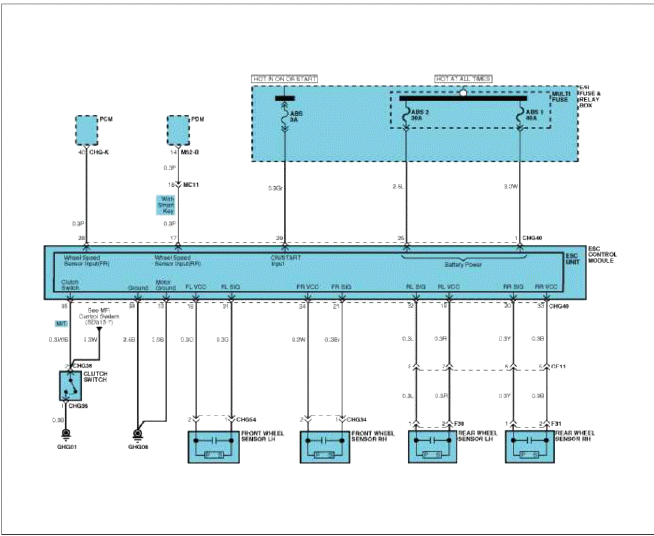
ESC connector input/output
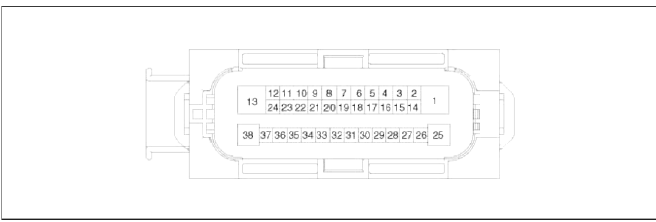

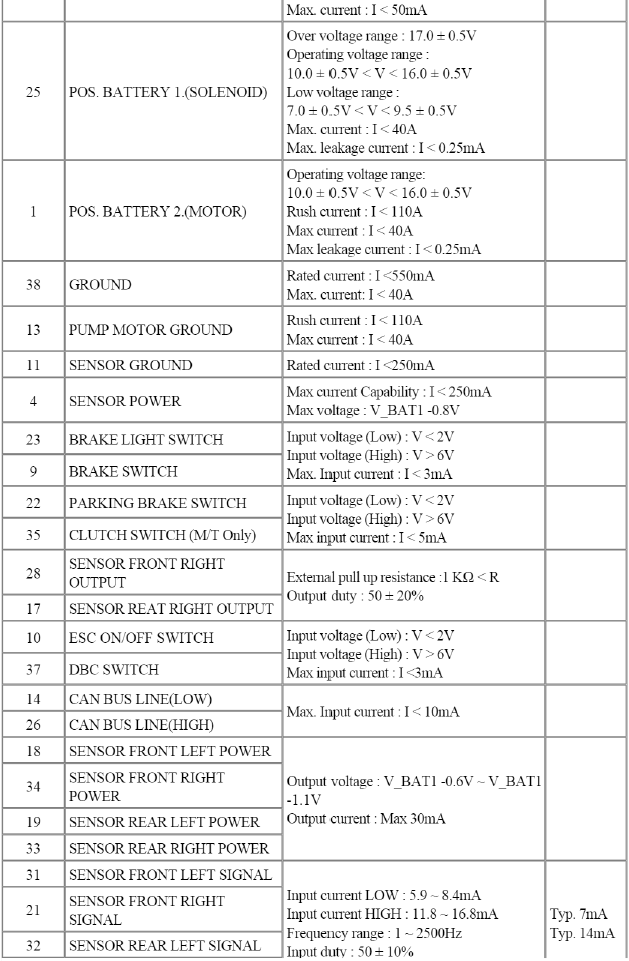
READ NEXT:
 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Failure Diagnosis
1. In principle, ESC and TCS controls are prohibited in case of ABS failure.
2. When ESC or TCS fails, only the failed system control is prohibited.
3. The solenoid valve rela
 EBD (Electronic Brake-force Distribution) | ESC Control Module
EBD (Electronic Brake-force Distribution) | ESC Control Module
Description and Operation
Operation
The EBD system (Electronic Brake force Distribution) as a sub-system of the ABS system is to control the maximum braking effectiveness by the rear wheels.
SEE MORE:
 Components and Components Location
Components and Components Location
Components Location
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS) #1
Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS)
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS) #2
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS)
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) [integrated into ETC
Module]
 Intake Manifold
Intake Manifold
Components and
Components Location
Components
Intake manifold
assembly
Electronic throttle body
Intake manifold stay
Intake manifold gasket
Repair procedures
Removal and Installation
1. Remove the engine cover.
2. Disconnect the battery negative terminal (A).
Tightenin
Content
- Home
- Kia Sportage - Fifth generation (NQ5) - (2022-2026) - Owner's Manual
- Kia Sportage - Second generation (JEKM) (2005-2015) - Body Workshop Manual
- Kia Sportage Third generation (SL) - (2011-2016) - Service and Repair Manual
- Sitemap
- Top articles